Amplitude Modulation
Communication Systems
The purpose of communication is to transmit information from one place to another. During the transmission process, a transmission channel or carrier is required. Wired communication systems use physical transmission lines, such as copper wires, optical fibers, etc., to conduct data transmission; wireless communication systems mostly use air or vacuum, utilizing electromagnetic waves (such as radio waves, microwaves, etc.) to conduct data transmission.
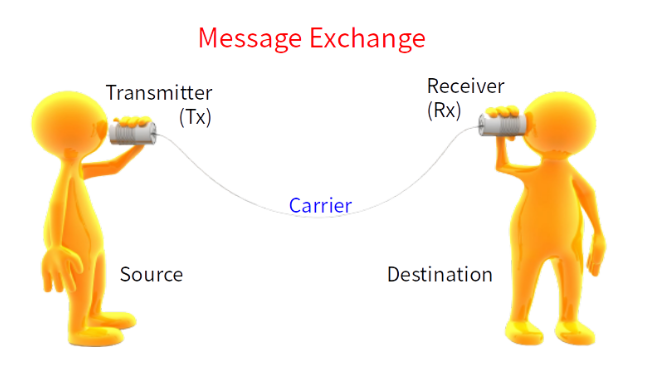
If the transmitted message is an analog signal, it is called analog communication; if it is a digital signal, it is called digital communication.
Modulation
Modulation is a signal processing technique, aimed at embedding signals (such as voice, data, or video signals) into a carrier signal, to facilitate transmission through the channel. Modulation can be achieved by altering any characteristic of the carrier, for example, in analog communication, adjusting the amplitude of the carrier signal is called Amplitude Modulation (AM); adjusting the frequency of the carrier signal is called Frequency Modulation (FM); adjusting the phase of the carrier signal is called Phase Modulation (PM).
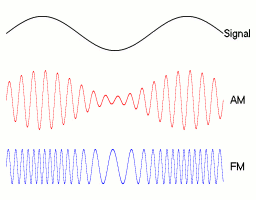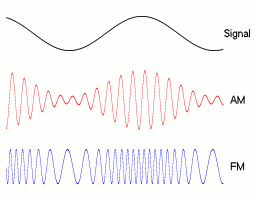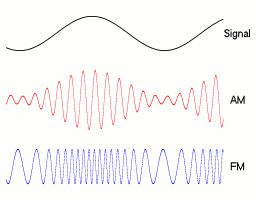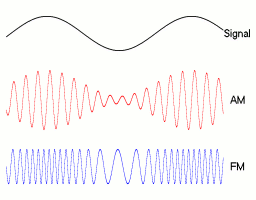
Exercise 1
What do you think a PM (Phase Modulation) signal might look like? Try to look it up and draw it out.
