FM Receiver
We will use the content learned in the previous section to build an FM receiver. Since we want to observe which possible FM channels are available within a certain frequency range, we use frequency shift and low-pass filtering for processing.
Construct an FM receiver as shown in the following figure:
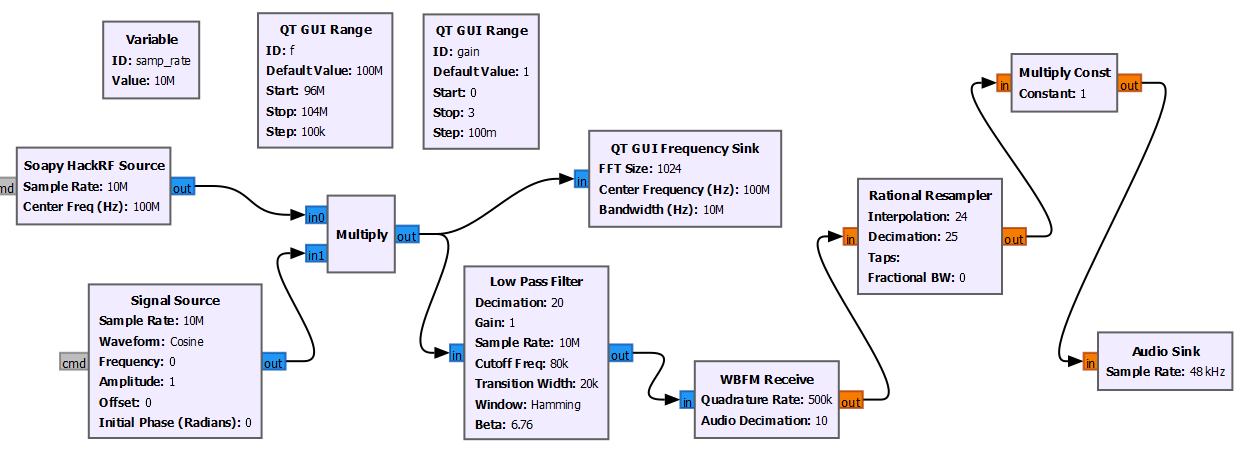
The parameters of each module are as follows:
- Soapy HackRF: Center Freq=100e6
- Range f=96e6~104e6
- Signal Source: Freq=100e6-f
- Low Pass Filter: Decimation=20, Cutoff Freq=80e3, Transition_width=20e3
- WBFM Receive: Quadrature Rate=500e3, Audio Decimation=10
- Rational Resampler: Decimation=25, Interpolation=24
- Range gain=0~3
- Audio Sink: 48e3
Here, when we perform low-pass filtering, we set Decimation=20, which means resampling a 10 MHz signal to 500 KHz. Then, decode through WBFM Receive and set Audio Decimation=10, which means the decoded Audio signal is 50 KHz. We then resample the 50 KHz signal to 48 KHz (50/25*24=48). Finally, we send the 48 KHz sound to the Audio Sink for playback (the frequency of the Audio Sink is also set to 48 KHz).
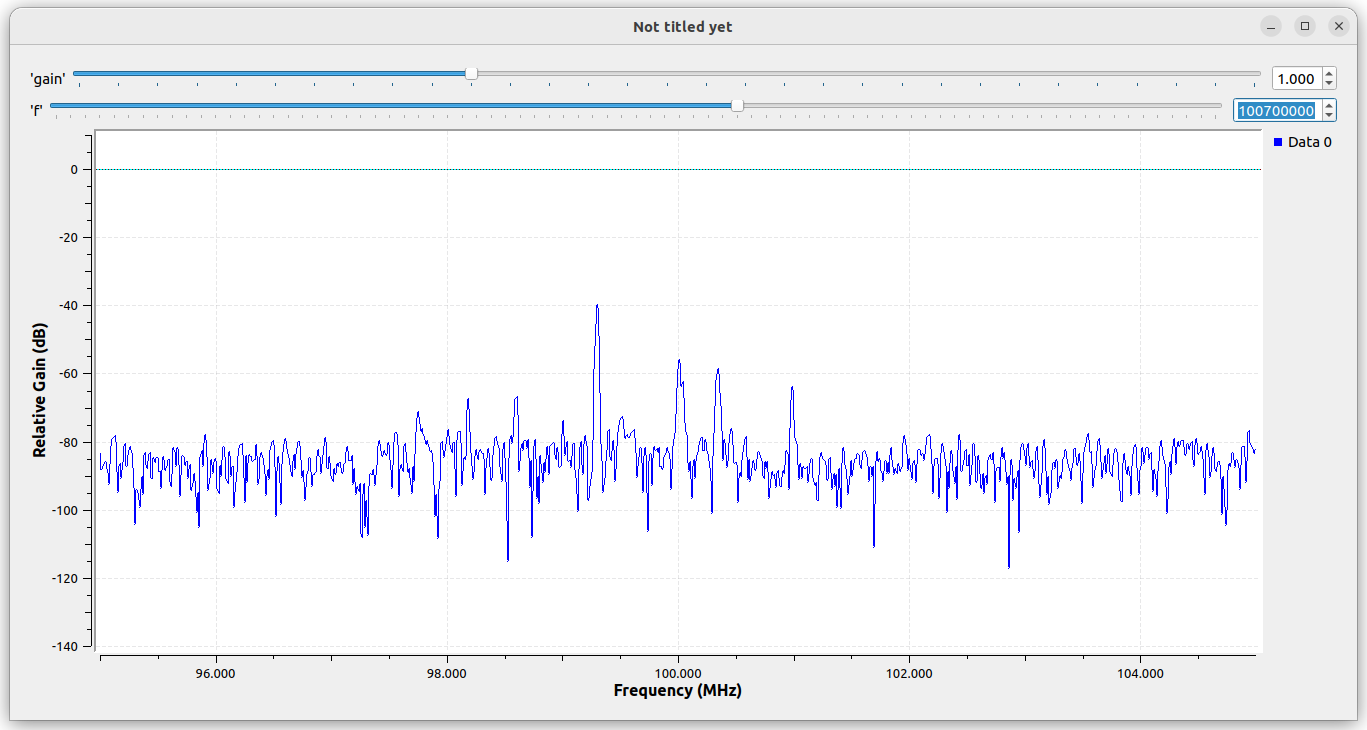
The simulation results are as follows (with f value of 100.7 MHz):
Exercise 4
- Try to complete the above simulation and adjust the frequency to see if you can hear the broadcast of an FM radio station.
- Try to redo the above simulation using a Frequency Xlating FIR Filter.
- Can you receive two FM radio stations simultaneously?
