Python 采样
2024年2月29日大约 1 分钟
Python 有很多套件可用,其中对于数据处理的部份,numpy 和 matplotlib 都是常被使用的套件,前者可用来处理各种矩阵运算,后者可以用来画图,这两个合起来,可以执行很多 MATLAB/Octave 程式的功能,而且语法非常相似。
我们一样假设信号频率为9,然后分别用采样频率100和10来观察信号采样的结果。程式码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the time vector for one second duration
t = np.arange(0, 1, 0.001) # Time from 0 to 1 second with 1ms interval
# Define the frequency of the cosine wave
f = 9 # Frequency of 9 Hz
# Generate the cosine wave
cosine_wave = np.cos(2 * np.pi * f * t)
# Plot the original cosine wave
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, cosine_wave)
plt.title('Original Cosine Wave (9 Hz)')
# Sample the cosine wave at 100 Hz
fs1 = 100 # Sampling rate of 100 Hz
n1 = np.arange(0, 1, 1/fs1) # Sample times
samples1 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * f * n1)
# Plot the sampled signal at 100 Hz
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.stem(n1, samples1, 'r', markerfmt='ro', basefmt=" ")
plt.title('Sampled at 100 Hz')
# Sample the cosine wave at 10 Hz
fs2 = 10 # Sampling rate of 10 Hz
n2 = np.arange(0, 1, 1/fs2) # Sample times
samples2 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * f * n2)
# Plot the sampled signal at 10 Hz
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.stem(n2, samples2, 'g', markerfmt='go', basefmt=" ")
plt.title('Sampled at 10 Hz')
# Show the results
plt.xlabel('Time (seconds)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()执行结果如下:
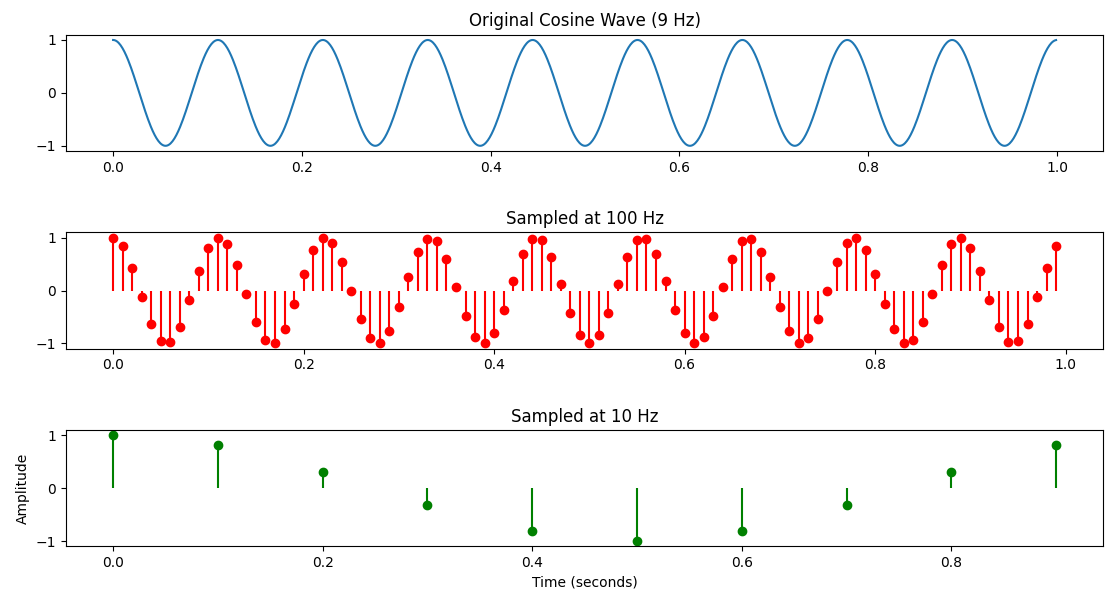
可以看到不管程式码,或者执行的结果,都和 Octave 的部份非常相似。
練習 4
练习安装上面所说的两个套件,并实际执行上述的程式码,观察结果是否相同。(建议用 Anaconda 或 venv 建立一个 Python 的执行环境,并用 pip install numpy matplotlib 安装套件)
