Sampling
What are Analog and Digital Signals?
Analog signals are continuous signals that have an infinite number of data points at any period, similar to sounds or light in the natural world.
Digital signals consist of discrete data points, with each data point taking a specific value at a specific time. These signals are suitable for computer processing and storage because they can be represented in binary form.
The Signal Sampling Process
Converting analog signals into digital signals involves two steps: sampling and quantization. Some textbooks mention that after quantization, there is also encoding, which relates to the issue of storage formats.
Sampling: Choosing the value of the continuous signal at specific time points, thereby converting an infinite number of data points into a finite number. This process is the first step in converting analog signals into digital signals.
The following diagram illustrates the sampling process:
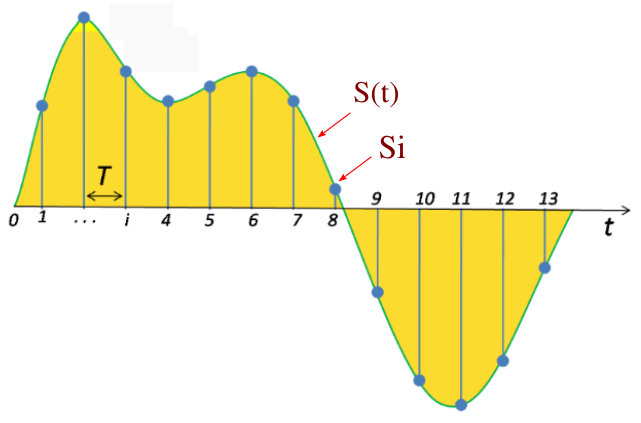
Quantization: Since digital systems can only represent a finite number of values, after sampling, the value of each sample point is converted to the closest predetermined digital value. This process is irreversible because it involves approximation, thereby introducing what is called quantization noise.
Exercise 1
Is the sampling process theoretically reversible? Explain your view and reasoning.
